Industry 4.0 technologies offer a safe, flexible and effective approach for leveraging change
By Arianna Todeschini, Corporate Business Development
If it’s easy to imagine a manager working remotely, it’s more complex to understand how this solution could be adapted to the manufacturing industry. The adoption of this model would involve a considerable effort in terms of productive infrastructure, but industry has always shown a great capacity for innovation.
In just over a hundred years, industry has gone from various revolutions that have seen the implementation of machinery and production lines, the use of electricity, computer automation, all the way up to the current revolution: smart manufacturing.
When we talk about ‘smart working’ in manufacturing, we’re talking about adopting intelligent solutions for the entire production cycle aimed at decreasing the time to market through process automation, improved working conditions, and the adoption of business plans that increase and improve the scope and production quality of manufacturing plants.
The adoption of smart factories, implementing a combination of smart production, smart service and smart energy, will become the solution for working effectively, safely and being able to respond to the demands of today’s market.
This revolution, that has seen impressive investment growth since 2015 (see the graph below), was born out of the intention of responding to the pressing need to be ever faster, more flexible, and capable of customizing the offer for the client; therefore allowing production to adopt mass customization systems.
In the two-year period of 2017–2018 alone, the Industry 4.0 revolution in Italy has generated 13 billion euros of investment and a wave of industrial facility modernization that shows no sign of slowing down in the near future (Source: Il Sole24Ore).
According to the latest research by the Smart Working Observatory at Milan’s Polytechnic University, over the next five years Italian companies will see some technologies essential to ‘smart’ production introduced on a massive scale.
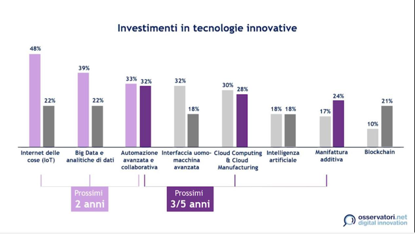
By dividing investments into two time horizons, it is possible to see how priorities will change.
If the focus is on IoT, Big Data and Advanced Automation in the first two years, in the following three it is estimated that investments in automation and growth in Cloud Computing & Cloud Manufacturing as well as Additive Manufacturing, will be a logical choice based on the sequencing of transformation and the maturity of innovations.
The new technologies—the researchers explain in the final report—enable profound changes in work organization (such as multi-channeling, 3D Printing or Artificial Intelligence).
It is estimated that, thanks to the use of these new technologies, the pool of workers who could perform the relevant tasks remotely would grow exponentially, to include almost all of Italy’s approximately 18 million salaried workers.

These changes take on manifold shapes as they continue to appear on the horizon and expand exponentially: IoT, additive manufacturing, robotics, bio and nanotechnology are just a few examples.
Smart manufacturing focuses on data sharing, using information to make technologies interconnected, allowing the remote control of plants and production chains, enabling big data analysis, making it possible to follow a project remotely, and having data available in real-time.
Using IoT, remote working, and cyber-physical systems, you can engage various company functions, as well as partners, customers and others, in order to produce more cost-effectively and create new work models.
